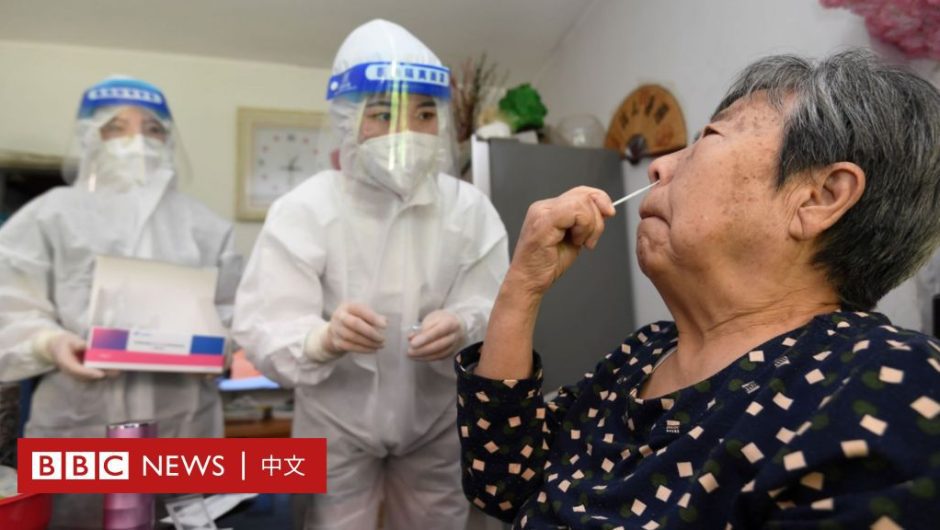
The magnitude 6 earthquake hit the high seas on Saturday at 2 pm local time at a depth of 82 km, 45 km from the city of Malang in East Java.
According to the Associated Press, citing local officials, at least seven people were killed and 12 others were injured. 300 buildings were damaged.
The records released showed a hospital roof collapsing as well as debris on the floor of the local parliament in Blitar, southwest of Malang. A resident told AFP that the quake “was very strong and it lasted for a long time.”
Several villages on the eastern coast of the island have been evacuated.
Repetitive trauma
Indonesia is located in the so-called Pacific Ring of Fire, a region of frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, consisting of a strip of ocean trenches, island arcs and active volcanoes, which surround the Pacific almost continuously for about 40,000 km. There are 452 volcanoes in this region and about 90 percent of all earthquakes in the world occur here.
In mid-January, a 6.2 magnitude earthquake jolted Celebes Island (Sulawesi). As a result, 56 people were killed. In 2018, an earthquake measuring 7.5 on the Richter scale off the coast of Celebes triggered a tsunami that devastated the Palau region and killed or disappeared more than 4,300 people. About 170,000 people lost their homes at that time.
The largest tragedy occurred off the coast of Sumatra on December 26, 2004. The massive tsunami waves, triggered by a magnitude 9.1 earthquake, killed more than 220,000 people in the entire region, including 170,000 in Indonesia alone. It was the greatest natural disaster in recent history.