A team of French physicists created a bubble based on water and glycerin that held its shape for 465 days. The scientists say their research could help develop new materials such as foams and membranes.

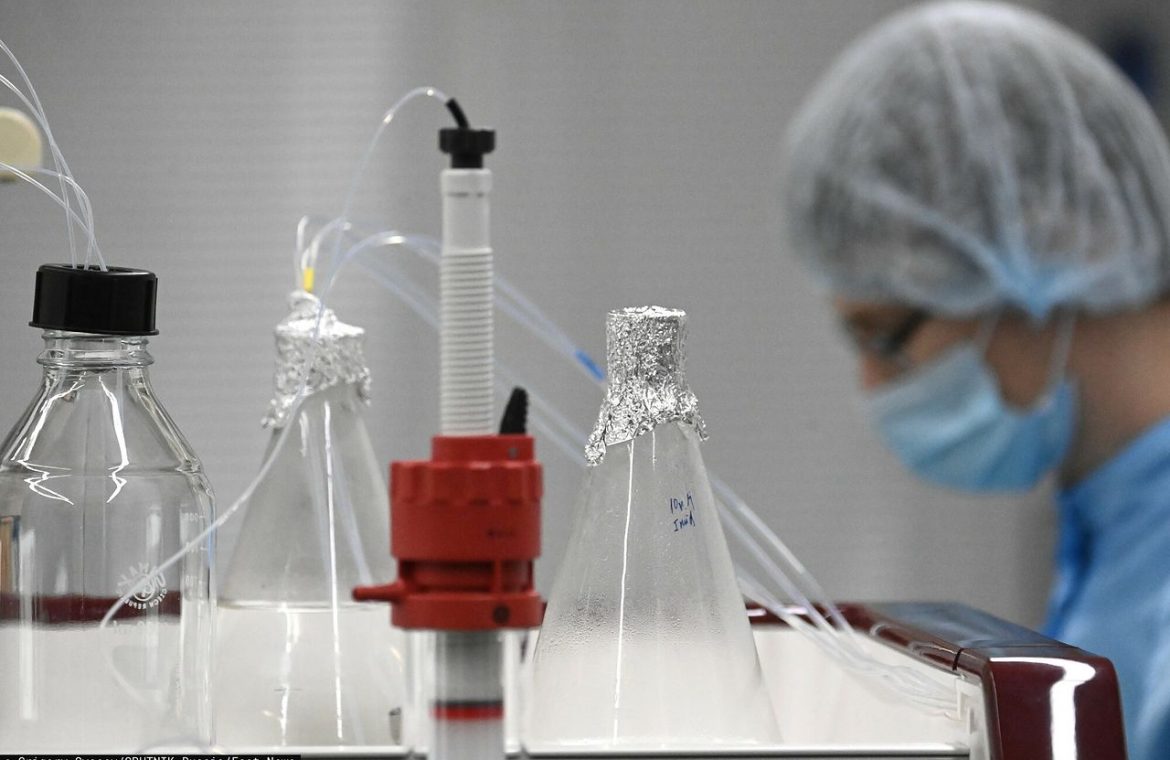
A team of physicists led by Emeric Roux of the University of Lille in France is responsible for creating the superbubble. During the research, scientists tested three types of bubbles: ordinary soap bubbles, gas balls based on water and nylon particles, and balls made of nylon particles and a mixture of water and glycerin.
Soap bubbles managed to maintain their integrity for a maximum of 1 minute, while water-based gas balls kept their integrity for 6 to 50 minutes. Meanwhile, glycerol and water bubbles were able to survive for more than 101 days. One of them retained its shape for 465 days.

Why do we lose our sense of smell with COVID-19? Scientists have discovered why

According to the researchers, this is due to the hygroscopic glycerin, which easily absorbs moisture from the environment or the atmosphere. This material also allows you to compensate for the evaporation of waterIt is one of the most common causes of bubble bursting. Nylon was also somewhat responsible for extending the life of the banks. The search was published in physical revision fluids.