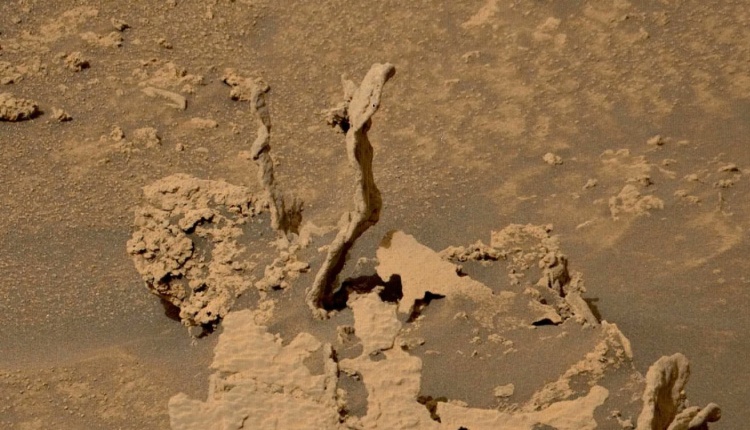
To photograph the surface of the Red Planet, NASA used a machine called the Curiosity Rover. It is not only a rover, but above all an automated and independent research and development laboratory. The device continuously performs various measurements (including meteorological) and checks the degree of soil moisture.
What does the picture show?
Interestingly enough, pictures of the unusual formation were taken 3474 on the day of the NASA mission. The representative of the SETI Scientific Institute decided to talk about her case.
According to a SETI expert, the photo was likely taken Cement fillings of old fissures in sedimentary rocks. As he claims – sedimentary rocks are made of sand and water, so the rest of the formation is made of a less durable material and gradually deteriorates.
Here is another interesting rock located in the crater of Mars Gale! The backbone is likely the cement fillings of ancient camel patches in sedimentary rocks. The rest of the rocks were made of a less durable material and eroded
– A spokesperson for the SETI Institute announced on Twitter.
#podHere’s another amazing rock in Gale Crater on Mars! The outcrops are most likely the cement fillings of ancient fractures in sedimentary rocks. The rest of the rocks were made of a softer material and eroded away. 📷: Tweet embed Tweet embed Tweet embed # mss fredk, acquired on May 17. pic.twitter.com/RGfjmRBfI7
SETIInstitute 26 May 2022
In addition, according to the portal Space.com, conditions on the Red Planet can also contribute to the formation of “more sensitive” rocks. The planet’s gravitational force is estimated to be about a third of that experienced by Earth’s inhabitants.
Source: niezalezna.pl, twitter.com, NASA, o2.pl

“Devoted organizer. Incurable thinker. Explorer. Tv junkie. Travel buff. Troublemaker.”