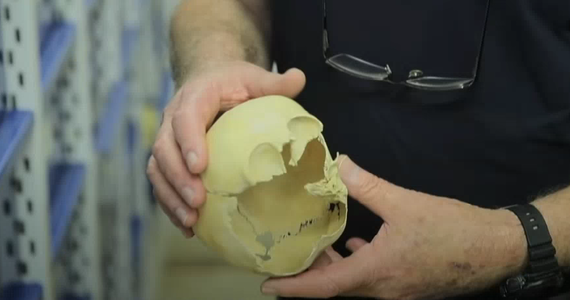
Representatives of previously unknown species inhabited the Middle East up to 130 thousand. Since years. The discovery was made at the archaeological site of Nesher Ramle near the city of Ramle (Israel).
Anatomical analyzes indicate that the Nesher Ramla man showed a similarity with more ancient representatives of the human race, whose history dates back to 400,000. years.
According to scientists from Tel Aviv University and the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, in terms of the lower jaw and teeth, the species is similar to Neanderthals, but in terms of the skull, it is closer to our species.
At the same time, scientists emphasize that it is highly unlikely that the remains belong to our species. This is evidenced by the large teeth and the lack of chin bones.
Scientists believe that the inhabitants of Nesher Ramla are the inhabitants with whom representatives of Homo sapiens intersected, when about 200,000 people arrived in this area. Since years.
Professor Israel Hershkowitz of Tel Aviv University describes: “The discovery of a new species within the genus Homo is of great scientific interest.”
The discovery was made during a salvage excavation. At a depth of eight meters, a large number of animal bones were found, including horses, fallow deer and larch, as well as stone tools and human bones.