Every day a lot of wonderful events happen aboard the cosmic house. For 20 years of operation, the facility has already been implemented Thousands of different experiencesThat contributed to the faster development of technologies that each of us deals with every day. Thanks to them, it will also be possible to take care of the health and safety of space tourists in orbital hotels and new space stations, and Future colonists of the Moon and Mars.
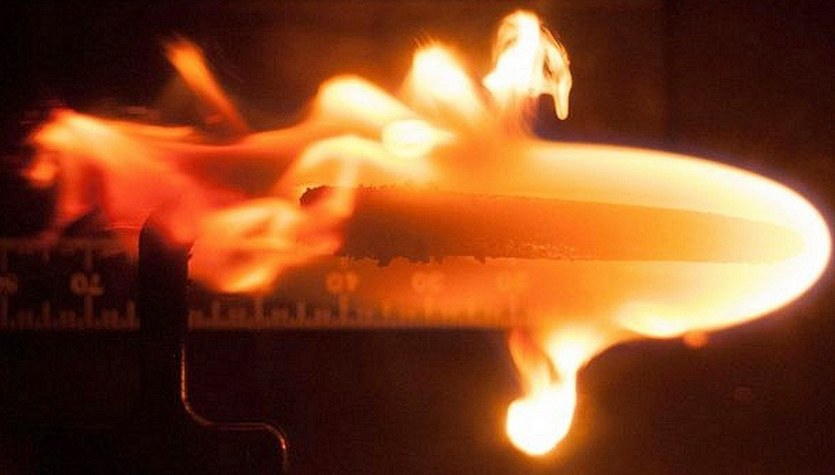
Another experiment was conducted just a few days ago. It’s called Solid Fuel Ignition and Extinction (SoFIE) i It’s about setting fire to space. Of course, in a controlled manner. Scientists admit that they were very surprised by the course of this test. Astronaut Thomas Marshburn began the experiment in a special 100-liter combustion chamber called Integrated combustion rackWhich is located aboard the US Destiny Laboratory unit.
This project will expand our knowledge on this topic The spread of fire on the roofs of the manned capsules and ships. The room is equipped with a number of sensors that detect oxygen and carbon dioxide levels, smoke concentration and volume, and temperature at various locations in the vehicle. Inside, four cameras were installed that showed the size and spread of the flame in real time.
Scientists report that elevated oxygen levels indicate Formation of flames more active. It’s similar on Earth, but not everything is the same. Although higher levels of oxygen speed up combustion, flames in space form and dissipate in a very different way than on the surface of our planet.
It relates to the properties of microgravity. On Earth, cold air descends while hot gases rise. Under conditions of weightlessness, such processes do not occur, so Gases are spherical in shape. Of course we’re talking about indoor spaces all the time, not the outer space itself, where there is a vacuum and a fire can’t break out.
This type of research is expected to help NASA develop better systems for detecting and suppressing space fires, and to investigate how Microgravity and limited oxygen affect the size of the flame. If we’re serious about manned flights to the Moon, Mars, Venus, and asteroids, protecting astronauts from fires that can break out on ships during long missions is a top priority.